📘 Unit 11 – Chapter 2
Human Reproductive System
🔶 What is Reproduction?
Definition:
Reproduction is the biological process by which a living organism (plant or animal) produces a new individual similar to itself. This helps in continuing the species.
🔶 Types of Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction:
- Involves both male and female.
- Requires fertilization (fusion of male and female gametes).
- Offspring are genetically different from parents.
- Asexual Reproduction:
- Involves only one parent.
- No fertilization needed.
- Offspring are exact copies (clones) of the parent.
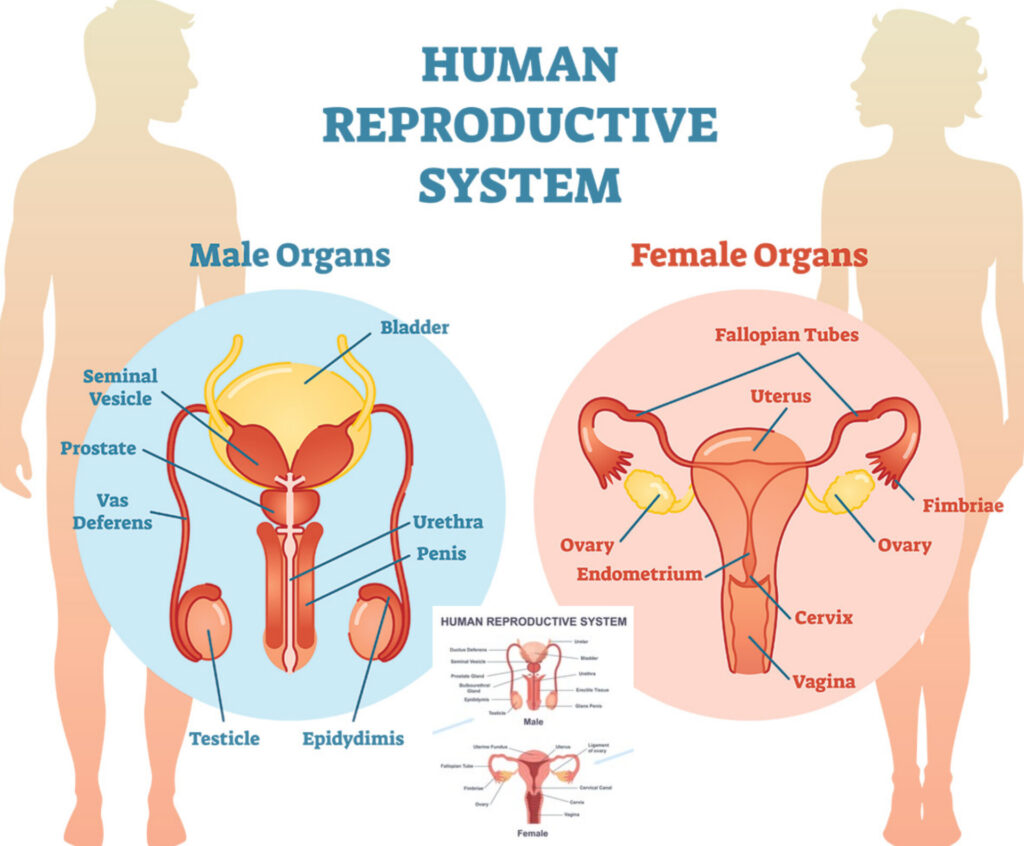
🔶 Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system has three main parts:
- External Genital Organs
- Internal Genital Organs
- Accessory Organs
✅ 1. External Genital Organs (Vulva)
These are visible from outside.
- Mons Pubis:
Fatty area above the pubic bone covered with pubic hair. - Labia Majora:
Outer lips or folds of skin protecting the genital area. - Labia Minora:
Inner folds of skin, present inside labia majora. - Clitoris:
Small, sensitive organ involved in sexual arousal. - Vestibule:
Triangular space between labia minora. Contains:- Opening of urethra (urine tube)
- Opening of vagina
- Ducts of Bartholin’s glands
- Skene’s glands
✅ 2. Internal Genital Organs
A) Vagina:
- Muscular tube (~8–9 cm long).
- Receives penis during intercourse.
- Passageway for menstruation and childbirth (birth canal).
Layers of vagina:
- Mucosal layer (inner)
- Submucosal layer
- Muscular layer
- Fibrous outer layer
B) Uterus (Womb):
- Hollow, muscular, pear-shaped organ.
- Site for embryo development and fetal growth.
- Size: ~7.5 cm long, weight: 50–80 grams
Parts of uterus:
- Fundus – top curved portion
- Body (Corpus) – main part
- Isthmus – narrow portion
- Cervix – lower part connected to vagina
Layers of uterus wall:
- Perimetrium – outer covering
- Myometrium – middle muscular layer
- Endometrium – inner lining (sheds during menstruation)
C) Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts):
- Tube connecting ovaries to uterus (~10 cm long).
- Site of fertilization (union of sperm and ovum).
Parts of Fallopian tube:
- Infundibulum – has finger-like fimbriae near ovary
- Ampulla – widest part, fertilization usually occurs here
- Isthmus – narrow, middle portion
- Intramural – part inside uterus wall
Function:
- Transports egg from ovary to uterus
- Helps sperm reach egg
- Carries fertilized egg to uterus
D) Ovaries:
- A pair of small, almond-shaped glands.
- Located on each side of uterus.
- Produce ova (eggs) and sex hormones (estrogen & progesterone).
Parts:
- Cortex: Outer layer – contains developing follicles (eggs)
- Medulla: Inner part – contains blood vessels, nerves
✅ 3. Accessory Organs
A) Bartholin’s Glands:
- Pair of glands near vaginal opening.
- Secrete fluid for lubrication.
B) Skene’s Glands:
- Near urethra. Also help in lubrication.
C) Breasts (Mammary Glands):
- Present in pairs, produce milk after childbirth.
- Contain 15–20 milk ducts opening at nipple.
- Surrounded by pigmented area called areola.
Functions:
- Milk production (lactation)
- Hormonal influence during puberty and pregnancy
🔶 Main Functions of Female Reproductive System
- Production of eggs (ova)
- Secretion of female hormones
- Site for fertilization
- Nourishment and development of fetus
- Menstruation and childbirth
- Milk production after birth
📝 Useful for Nursing Students:
- Understand structure & function of reproductive organs
- Know hormonal changes and menstrual cycle
- Learn about pregnancy, labor & postnatal care
- Apply knowledge in gynecology, obstetrics & maternal care
