Type of Joint
- Synovial Ball-and-Socket Joint (सायनोवियल कंदुक-खल्लिका संधि)
- Multiaxial movement: Flexion, Extension, Abduction, Adduction, Rotation, Circumduction.
BONES INVOLVED
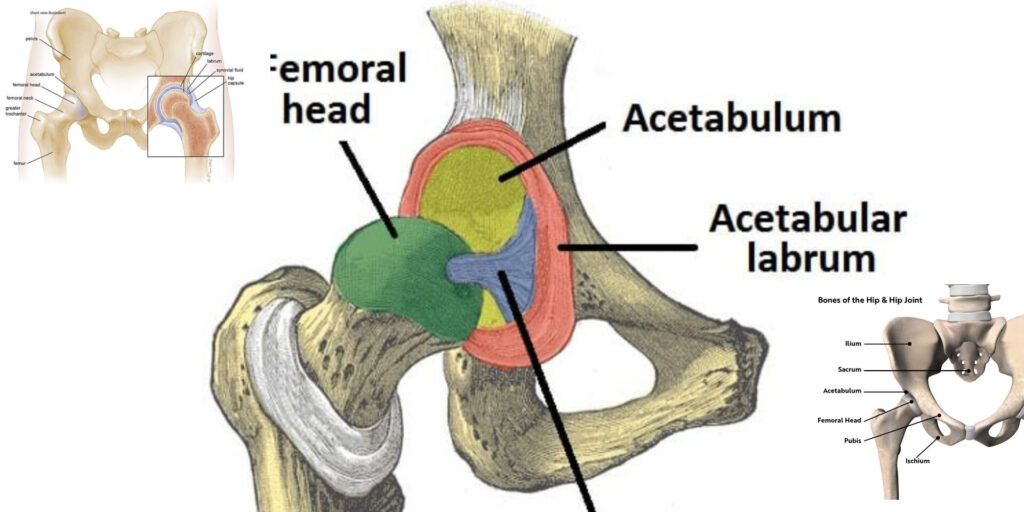
- Acetabulum (असेटाबुलम)
- Formed by the fusion of ilium, ischium, and pubis.
- Lunate surface (चंद्राकार सतह) is covered with hyaline cartilage.
- Acetabular labrum (असेटाबुलर लेब्रम) deepens the socket for stability.
- Femur (फीमर)
- Head (फीमर का सिर) – Articulates with acetabulum.
- Neck (गर्दन) – Common site for fractures (especially in osteoporosis).
- Greater & Lesser Trochanter (ग्रेटर और लेसर ट्रोकैंटर) – Muscle attachment sites.
LIGAMENTS (स्नायुबंधन)
1. Intracapsular Ligament
- Ligament of Head of Femur (लिगामेंट टेरिस फीमोरिस)
- Contains acetabular artery branch (minor blood supply to femoral head).
2. Extracapsular Ligaments (Provide stability)
- Iliofemoral Ligament (इलियोफीमोरल स्नायु)
- Strongest ligament in the body (“Y-shaped”).
- Prevents hyperextension.
- Pubofemoral Ligament (प्यूबोफीमोरल स्नायु)
- Limits excessive abduction.
- Ischiofemoral Ligament (इस्कियोफीमोरल स्नायु)
- Reinforces the posterior capsule.
BLOOD SUPPLY (रक्त आपूर्ति)
1. Medial & Lateral Circumflex Femoral Arteries
- Main supply to femoral head (especially lateral circumflex).
- Injury risk in femoral neck fractures → Avascular necrosis (AVN).
2. Artery to Head of Femur (Obturator artery branch)
- Minor contribution (often insufficient alone).
3. Femoral Artery (फीमोरल धमनी)
- Supplies surrounding muscles and soft tissues.
MUSCLES & MOVEMENTS
| Movement | Major Muscles |
|---|
| Flexion | Iliopsoas, Rectus femoris, Sartorius |
| Extension | Gluteus maximus, Hamstrings |
| Abduction | Gluteus medius & minimus |
| Adduction | Adductor longus, brevis, magnus |
| Medial Rotation | Gluteus medius & minimus (anterior fibers) |
| Lateral Rotation | Piriformis, Obturator externus/internus |
CLINICAL CORRELATIONS
1. Hip Fractures (कूल्हे का फ्रैक्चर)
- Femoral Neck Fracture → Risk of AVN due to disrupted blood supply.
- Intertrochanteric Fracture – More stable (better blood supply).
2. Developmental Dysplasia of Hip (DDH)
- Congenital dislocation due to shallow acetabulum.
- Tests: Ortolani & Barlow maneuvers.
3. Trendelenburg Gait
- Weak gluteus medius → Pelvis drops on opposite side during walking.
4. Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Degenerative joint disease → Pain, stiffness, reduced mobility.
SUMMARY TABLE
| Feature | Description |
|---|
| Joint Type | Ball-and-socket synovial joint |
| Main Ligaments | Iliofemoral, Pubofemoral, Ischiofemoral |
| Blood Supply | Medial/Lateral Circumflex Femoral Arteries |
| Common Injury | Femoral Neck Fracture → AVN |
Diagrams to Remember:
- Hip Joint Ligaments (Iliofemoral “Y” shape).
- Blood Supply to Femoral Head (Medial & Lateral Circumflex).
- Muscle Actions (Flexors vs. Extensors).
Kritika Group Of College, Bareilly

